Table of Contents
What are macronutrients?
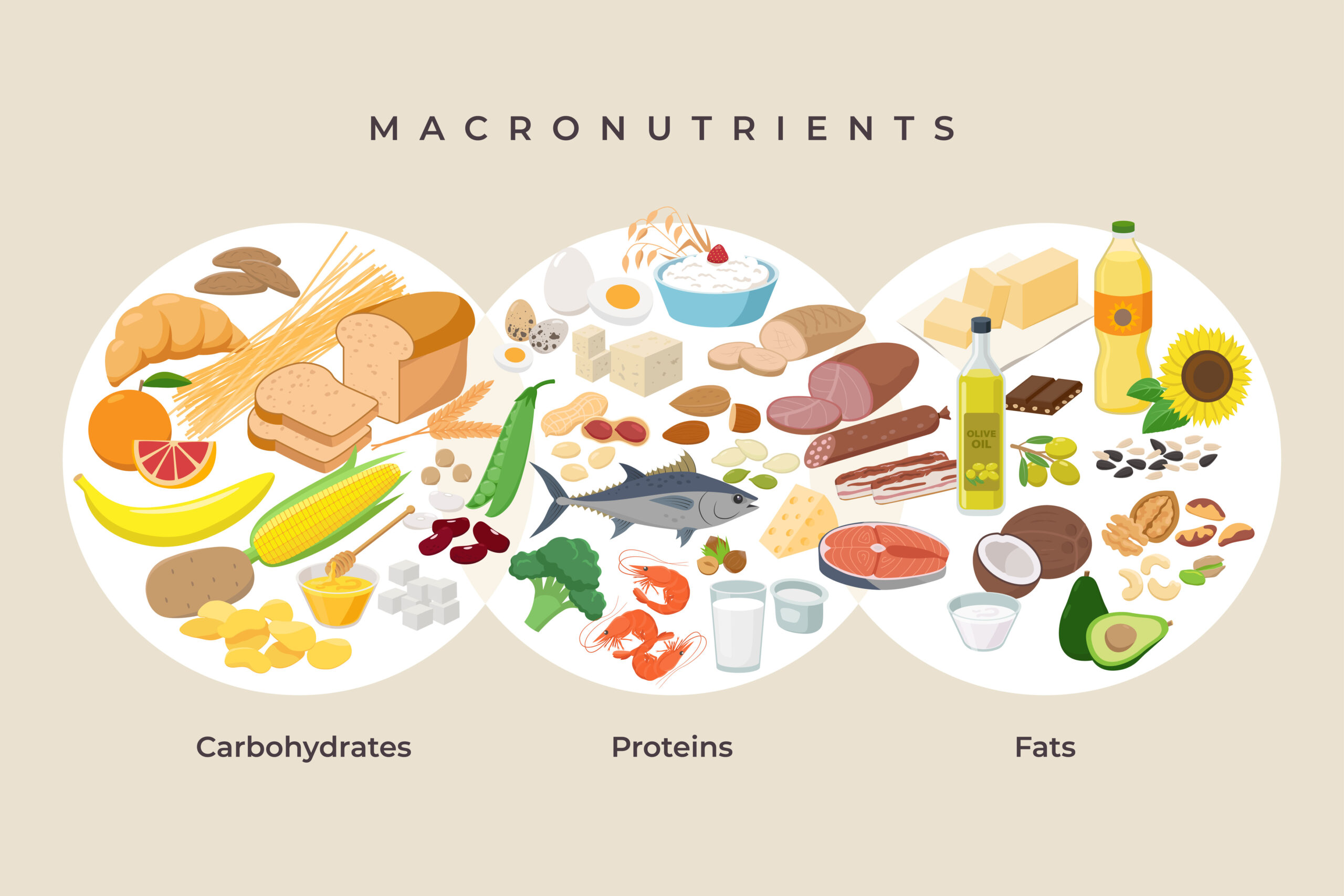
Macronutrients are the essential nutrients that our bodies need to function properly. They are the building blocks of a healthy diet and are necessary for the body to maintain good health, energy, and vitality. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the three main macronutrients and explain why they are important for a healthy balanced diet.
The Protein Macro

Protein is one of the three essential macronutrients, along with carbohydrates and fats, that our bodies require in large amounts for optimal health and function. While all macronutrients play important roles in the body, protein is particularly crucial because it is used to build and repair tissues, create enzymes and hormones, and support the immune system. Without this nutrition, the body would find it much more difficult to build muscle and repair damage. This makes the protein macro a vital part of a healthy diet.
What is the protein macronutrient?
First, let’s define what the protein macro is. Protein is a molecule made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of life. There are 20 different types of amino acids, and our bodies can create some of them on their own, but others, known as essential amino acids, must be obtained from the nutrition in the foods we eat.
Protein is found in a wide variety of foods, including meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, beans, nuts, and seeds. It is important to consume a variety of protein sources to ensure that you are getting all of the essential amino acids and nutrition that your body needs.
Why is protein good for your health?
One of the main functions of the protein macro is to build and repair tissues. When we engage in physical activity or experience an injury, our muscles and tissues may become damaged. Protein is essential for repairing this damage and helping our bodies recover. This is why athletes and bodybuilders often consume high amounts of protein to support their muscle growth and recovery.
Protein is also essential for creating enzymes and hormones. Enzymes are molecules that help to catalyze chemical reactions in the body, while hormones are chemical messengers that help to regulate various bodily processes, including metabolism, growth, and development.
Finally, protein is essential for supporting the immune system. Antibodies, which are proteins, are the body’s first line of defence against infections and diseases. They help to identify and neutralize harmful pathogens and keep us healthy.
In addition to these critical functions, protein also helps to promote feelings of fullness and can aid in weight management. Because protein takes longer to digest than carbohydrates or fats, it can help to keep you feeling full for longer and may reduce your overall calorie intake.
It is important to note that while protein is important, consuming too much of it can also have negative health effects. Excessive protein consumption can put a strain on the kidneys and increase the risk of osteoporosis.
In conclusion, protein is a crucial macronutrient that plays many important roles in the body. It is important to consume a variety of protein sources and to aim for a balanced intake to support optimal health and function. Whether you’re an athlete, trying to manage your weight, or simply looking to support your overall health, protein is a nutrient that you shouldn’t overlook to maintain a healthy body.
The Carbohydrate Macro

Carbohydrates are the second of the three essential macronutrients, along with protein and fat, that the human body requires in large amounts for optimal health and function. Despite the recent popularity of low-carb diets, carbohydrates are an important source of energy for our bodies and provide many other health benefits.
What is the carbohydrate macro?
First, let’s define what carbohydrates are. Carbohydrates are molecules made up of sugars, such as glucose and fructose. They are found in a wide variety of fresh food, including fruits, green vegetables, grains, and legumes. Carbohydrates can be divided into two categories: simple carbohydrates, which are made up of one or two sugars, and complex carbohydrates, which are made up of many sugars linked together.
Why are carbohydrates good for your health?
One of the main functions of carbohydrates is to provide energy for the body. When we consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which our cells use as a source of fuel. Carbohydrates are especially important for high-intensity exercise, as they provide a quick energy source for our muscles.
Carbohydrates also provide essential nutrients, such as fibre and vitamins. Fibre is a type of carbohydrate that is not digested by the body but instead helps to promote digestive health and regulate blood sugar levels. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are all good sources of fibre. Additionally, many fruits and vegetables are high in vitamins and minerals that are important for overall health.

While carbohydrates are important, choosing the right types of carbohydrates is essential. Simple carbohydrates, such as candy and sugary drinks, provide a quick energy source but can lead to blood sugar spikes and crashes. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and legumes, provide a slower, more sustained energy source and are also higher in fibre and other vital nutrients.
It is also important to pay attention to portion sizes and to balance carbohydrate intake with other macronutrients. Consuming too many carbohydrates, especially in the form of refined and processed foods, can lead to weight gain and other adverse health effects.
In conclusion, carbohydrates are an essential macronutrient that provides energy, supports brain function, and provides important nutrients. Choosing the right types of carbohydrates and balancing carbohydrate intake with other macronutrients can help to support overall health and well-being.
The Fat Macro

Fats are the final of the three essential macronutrients, along with carbohydrates and protein, that the body requires in large amounts for optimal health and function. Despite their bad reputation, namely, for not being healthy and creating unwanted body fat, this macro is an important nutrient that provides many health benefits.
What is the fat macro?
First, let’s define what fats are. Fats are a type of nutrient that is used by the body for energy, insulation, and protection of internal organs. They are found in various foods, including oils, nuts, seeds, meats, fish, and dairy products. The fats macro can be divided into three categories: saturated fats, unsaturated fats, and trans fats.
Why are fats good for your health?
One of the main functions of fat is to provide energy for our bodies. Fat is a concentrated energy source, providing 9 calories per gram compared to 4 calories per gram for carbohydrates and protein. Fat is especially important for endurance exercise, as they provide a long-lasting energy source for our muscles.
Fat also plays a role in the absorption of vitamins and minerals. Many vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K, are fat-soluble, meaning that the body can only absorb them in the presence of fat. Fat also helps to transport these vitamins and other nutrients throughout the body.
In addition to providing energy and aiding in nutrient absorption, fat also plays a role in brain function. The brain comprises about 60% fat, and studies have shown that low-fat diets can lead to impaired cognitive function.
While fat is important, not all fat is the same. There are several different types, and it is important to choose the right fats for a healthy diet. Saturated fats, which are found in animal products and some plant-based oils, have, in some studies, been shown to increase the risk of heart disease when consumed in excess. Unsaturated fats, which are found in plant-based oils, nuts, and fish, can help to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease when consumed in moderation. There is much debate about the effect of dietary cholesterol, enough for several blogs!
Trans fats, which are found in processed foods such as baked goods and fried foods, should be avoided as much as possible. Trans fats have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and other health problems.
In conclusion, fat is an essential macronutrient that provides energy, aids in nutrient absorption, and supports brain function. Choosing the right types of fats and consuming them in moderation can help to support overall health and well-being. Whether you’re an athlete or simply looking to maintain a healthy diet, fat is a nutrient you shouldn’t overlook.
Summary
While each macronutrient serves a unique purpose in the body, it’s important to consume a balanced diet that includes all three. This can help ensure that the body receives all of the nutrients it needs to function optimally. Additionally, understanding the role of each macronutrient can help individuals make informed dietary choices to support their overall health and wellness.